Polishing pad: the most important tool for polishing
Special tools are needed to buff and polish surfaces. A polishing machine can be used to give surfaces a new look. The polishing pads are placed on the polishing machine to do the actual work. We have collected the most important things to know about it in our current article.
Types of polishing machine
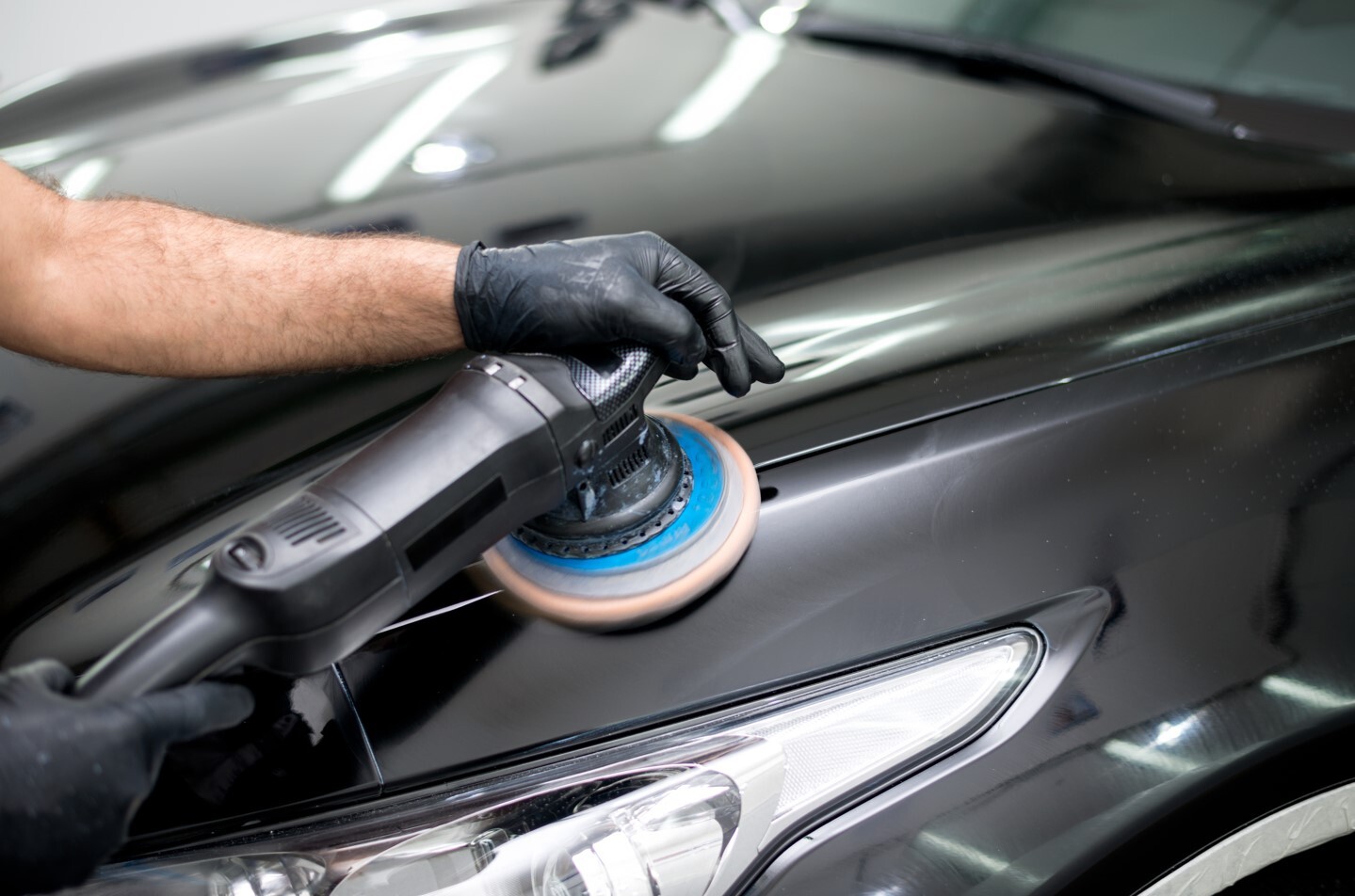
A polishing machine, although very similar, is different from an angle grinder. These machines are considered entry-level tools. Should you be puzzled about what to use for a specific polishing project, start with this one. There are also pneumatic electric polishers, which represent the professional category. They have the advantage of much smoother operations due to the oscillating movement. These are more expensive than entry-level machines, but they provide much better results.
When choosing the optimal tool, the amount of daily use is important. If you use it a lot, it is advisable to choose a lighter model so that your hands endure less opposition during polishing. This is particularly important, as the operator's movements will be the result. Equally important is the noise level of the machine, especially when used outside of the industrial environment. Polishing can be carried out using both electric and battery-powered polishers.
The polishing pads
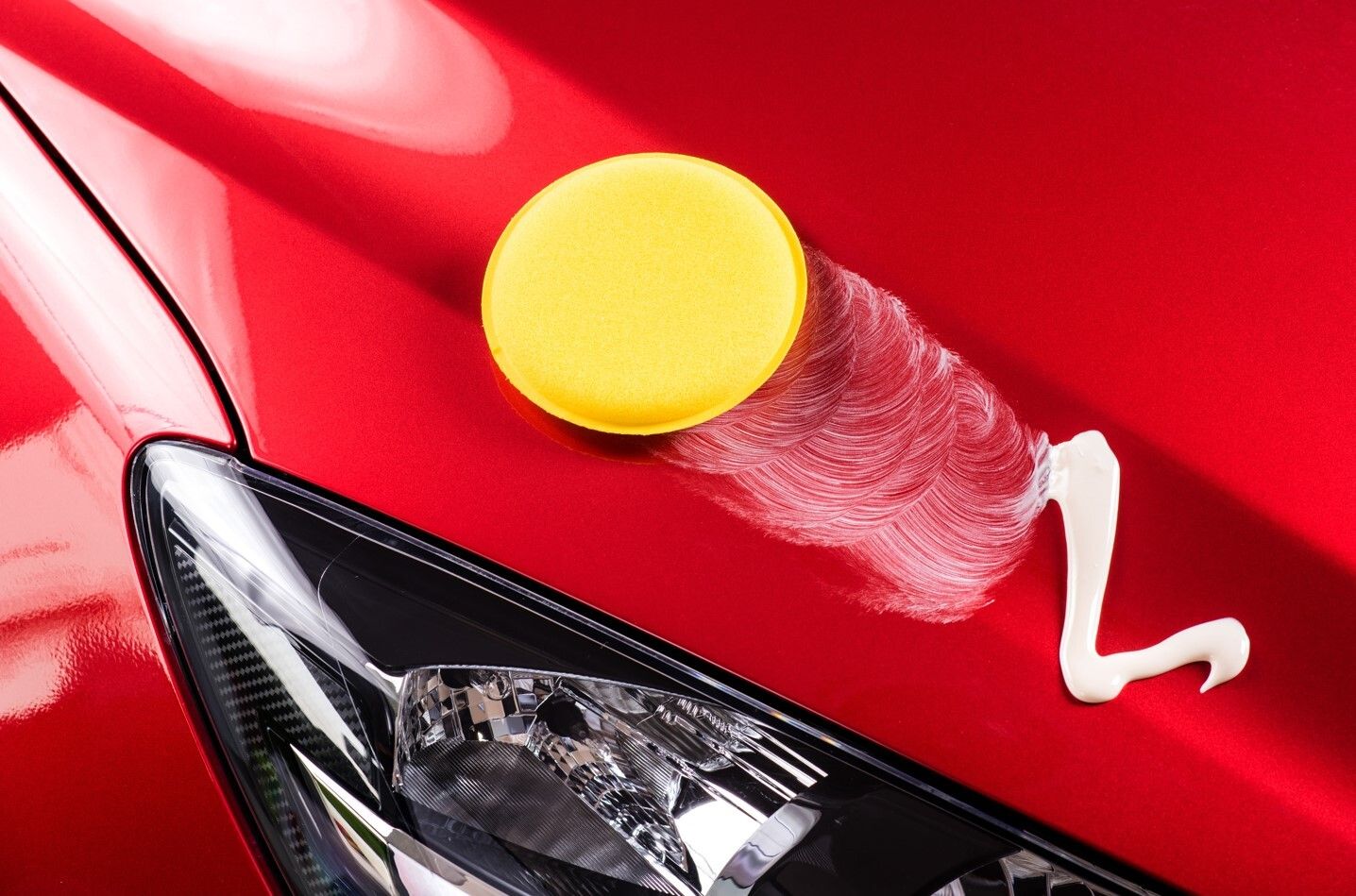
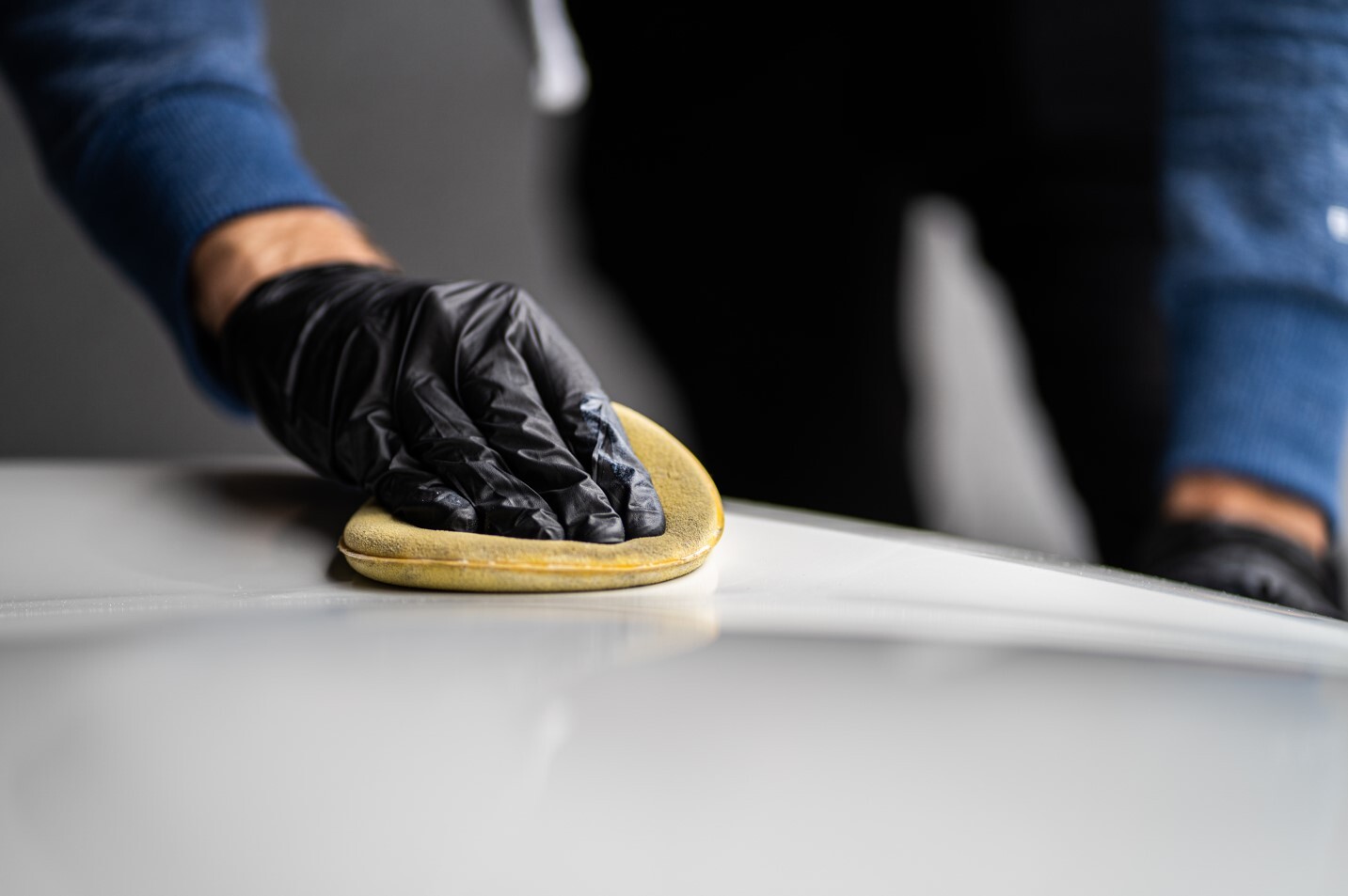
The polishing pad, also known as the buffing pad, is a soft disc-shaped pad that is placed on the polishing machine to do the actual polishing. The pads come in different colours that indicate the strength of the disc. For the finest work, blue is recommended, followed by orange, white and finally black.
There are many applications for which different polishing pads are recommended. Some are specifically designed to remove polishing marks and achieve a high gloss finish. Others are fine finishing pads for accurate results. Some pads are used to repair scratches and damage caused during the manufacturing processes. Finally, there are pads for simple dirt-removing tasks.
The surface varies, with some pads having a convoluted, grooved surface. The material can change too, as some pads are made of wool. Pads can differ according to the attachment logic too.
Polishing fluids are essential during the process. This special fluid substance ensures that the polishing process achieves its purpose, for example, to remove all the fine scratches from the surface of the vehicle. There are polishing compounds that are specifically designed to remove scratches, some that are used to clean headlights, and some that are used to polish aluminium and chrome parts.
Polishing in practice
Polishing is the process of removing scratches. In general, we differentiate three separate stages. During the first one wider damages are removed and then comes the elimination of medium-level scratches, which is followed by the eradication of broom scratches. Three types of pads and polishing fluids should be used during this process, one for each separate step.
Try a slower speed of 700 rpm at the beginning, on a smaller surface. It is best to continue advancing at a steady pace, or slow pace, moving the polisher back and forth and left and right. It is important to keep changing the pads. Let them rest and make sure they are cleaned properly. It is important to bear in mind that the polishing capability of the pad will diminish over time, so switching from slow to fast speeds, using more polishing material or applying more pressure to the machine is not the answer. This is why continuous replacement is necessary.
The cleaner the pad, the better the result. As the pad traps the paint and the polishing fluid too, it is worth cleaning regularly. The pads can be washed in a washing machine but can also be cleaned very effectively using dry air. However, they should not be dried on radiators or stoves as their structure does not react well to heat.
Used pads should therefore not be thrown away, but be aware that as they wear, they will provide diminishing results over time.
Check out our web catalogue for our polishing products.
- Hits: 674